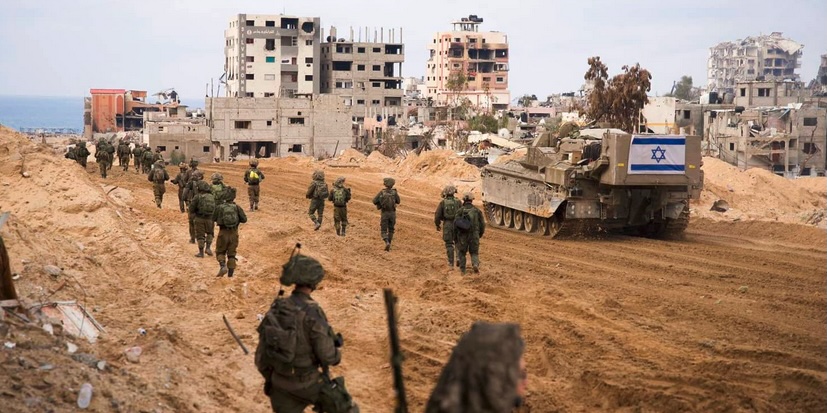
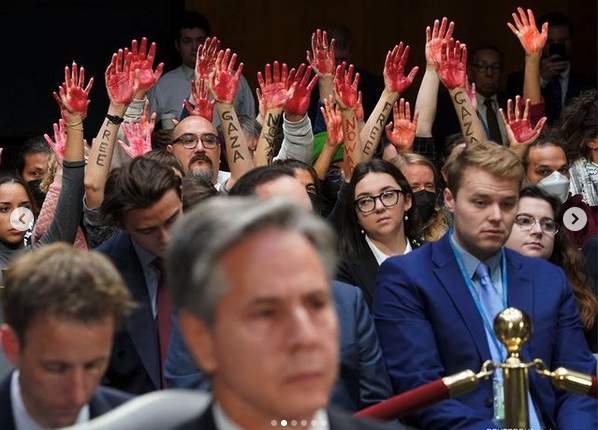
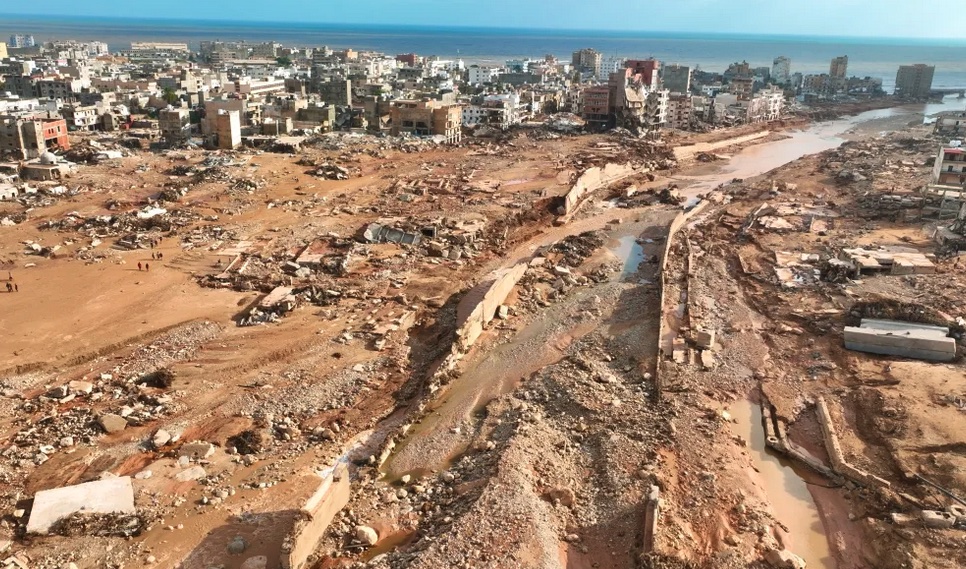
In Gaza today, we see Israel’s cruel, violent, and always ‘West’-backed military working overtime to snuff out the existence of the Palestinians in Gaza and the West Bank, two areas that have always formed a key part of Palestinian national territory. This phenomenon is not new in the lengthy record of the actions that heavily armed, West-European-origined settler cohorts have taken against the Indigenous people of lands far from the shores of Western Europe. Indeed, it replays with disturbing accuracy the actions that violent Portuguese, Spanish, English, Dutch, and French adventurers took over the past 500 years against Indigenes in the Americas, Africa, Asia, Australasia.
But today, everyone worldwide can see this latest massacre of the Indigenes taking place in all-color video, in near-real time.
That vast, non-‘Western’ majority of humankind whose ancestors were the survivors of earlier White-Western settler rampages well understands what is going on, and stands aghast at the continuing, barbaric cruelty of the Israeli government and military– and also at the active complicity of the U.S. and many/most other Western governments. (Many citizens of those complicit Western countries are also aghast at the massacre in Gaza, though a disturbing proportion of them– of us– have been cowed, silenced, and blackmailed by the endless repetition of old tropes about the need for Westerners and others always to “support Israel.”)
It is ways past time for all of this– above all, the massacres themselves, but also the complicity and the silence– to end.
I have been actively calling, since early November 2023, for the United States to step aside from the lockhold it has exercised since 1990 (or earlier) on all dimensions of Arab-Israeli “peace-making.” By wielding this lockhold, successive U.S. presidents have not just allowed but also actively supported Israel’s continued suppression of Palestinian rights, its force-backed takings of Palestinian and Syrian territory, and its repeated wars against neighbors.
At the end of that earlier essay I noted that in 1956, an earlier U.S. president, Dwight Eisenhower, had intervened against the British, French, and Israeli governments to force them to reverse the large-scale land-grab they had just undertaken against Egypt. And Eisenhower achieved that laudable goal not through military action (though he had earlier been been a forceful and effective military commander.) Rather, he did it by using only economic pressure, flexing just a small portion of the dominance the United States enjoyed in the world economy back then, to bring those three aggressive rogue states to heel. (Tragically, their Tripartite Aggression of 1956 had harmed not only numerous Egyptian military and civilian installations but also the always vulnerable, overwhelmingly civilian population of Gaza, who also stood in Israel’s way…)
In my essay I noted that just a few days later, in mid-November 2023, the leaders of the United States and China would be meeting in San Francisco. And I asked whether that meeting might see some efforts to restore oversight over Arab-Israeli peacemaking to the United Nations, where it rightfully belongs, and to end the (sharply pro-Israel) U.S. oversight of that diplomacy.
That did not happen then, and it hasn’t happened since– despite so many of us having continued to call, with increasing urgency, for the world powers to decisively END the political protection and the active support that Washington and its minions have given to Israel’s genocide in Gaza.
Like the vast majority of other governments around the world, the People’s Republic of China has been strongly critical of that genocide since the beginning, as it had been of Israel’s many other violations of international law against Palestinians and others, for many decades prior. But Beijing has still taken zero visible or effective action, of the kind that Eisenhower took back in 1956, to rein in the US-Israeli assault on Gaza and push Israel back to its recognized international border.
In March, researcher Zhang Shen published this excellent analytical essay about China’s policy on Palestinian, in Mondoweiss. In it he wrote,
The seemingly promising bilateral [trade-focused] relationship between China and Israel from 2015 to 2020, once created some voices, both within Chinese and Israeli society, calling for a deeper strategic cooperation between the two states. Yet, what happened on 7 October 2023, and in particular the Israel bombardment of Gaza that followed, irreversibly destroyed the possibility of business as usual.
Right after 7 October, the Israeli government demanded China condemn Operation Al-Aqsa Flood and to list Hamas as a terrorist organization, but unsurprisingly, China refused this demand. The Chinese government does not accept the Western-Israeli narrative that portrays 7 October as the start of history. Instead, China sees it as one of the many tragedies of the prolonged “Arab-Israeli conflict” inherited from British colonial rule. The PRC, as a regime that emerged out of Mao’s strategy of “people’s war,” guerrilla warfare, and anti-colonial armed struggle, remains inherently sympathetic toward other guerrilla forces of the Global South.
But still, until now, the PRC government has taken no concrete steps to end Israel’s genocide in Gaza or to challenge the “ironclad” protection and support that Washington has given to the génocidaires.
I guess there are a number of possible explanations. Maybe the CCP’s leaders do not care enough about what’s happening to Palestinians in Gaza to try to take action? Or– and this I find more likely– maybe they care very deeply but are still for a number of reasons wary of confronting Washington over an issue that, as they must understand, the powers-that-be in Washington have long judged to be of central importance to them.
Whether, when, and how, we might see some change in these judgments in Beijing (or, more accurately, in the well-guarded Zhongnanhai enclave where CCP leaders hold their most important conclaves) is what I’ll be exploring in the remaining portions of this series.
This is a matter of impact far beyond the misery-soaked ruins of Gaza. That tiny enclave is now the epicenter of the “last gasp” of the White/Western supremacist worldview that has dominated world affairs for the past four-plus centuries. What happens there matters to all of humanity.