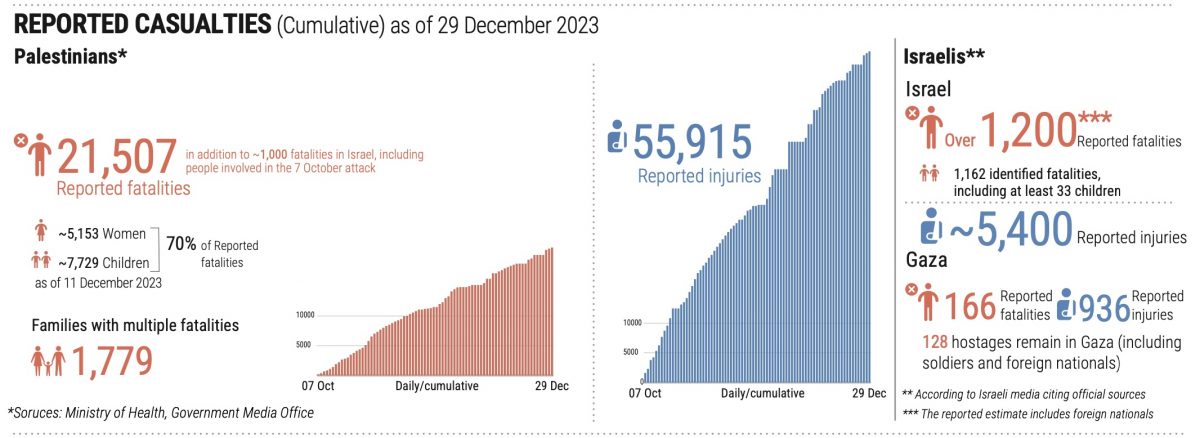
The photo above, by Maureen Clare Murphy, shows a kite displayed at a memorial gathering held in Chicago for my friend the assassinated Gaza writer Refaat Alareer
I haven’t written much here recently. In the past two months I’ve been really busy with the book-publishing business, from which I’d earlier hoped I could start to retire. But my publishing company, Just World Books, has long had a strong list of titles on Gaza, and by Gaza-Palestinian authors, so there’s been a huge run on our books… Plus, on December 6, our wonderful author/editor Refaat Alareer, a professor of literature at the Islamic University of Gaza, was assassinated by Israel; and I’ve been doing what I could to defend his legacy and ensure that the works he edited (and contributed to) get as wide a distribution as possible.

I have also been working on a longer essay for a national publication about the clearly massive impact the Gaza crisis has already had, and will continue to have, on the dynamics of global power. Stay tuned for that… Oh, and with my dear Gaza-Palestinian colleague Dr. Yousef Aljamal and a talented new Irish pal called Tony Groves we’ve gotten our new Palestine-focused podcast, the PalCast, up and running. Hey, we’ve now released eighteen episodes of it! (Catch it at Apple, Spotify, or other good podcast platforms.)
So of course this means I’ve continued to follow all the developments unfolding in (and swirling very broadly around) the Gaza crisis pretty closely. I’ve also been networking with numerous other individuals and organizations that are pushing for a speedy ceasefire there and the launching of a serious, U.N.-led project to end Israel’s occupation of Gaza, the West Bank (including E. Jerusalem), and Golan, once and for all.
In these contacts, I’ve encountered quite a few people outside Gaza who admit to feeling “hopeless” to effect change there; and many of those people, and others, frequently express pity for the situation of the 2.3 million people of Gaza. I’ve thought quite a lot about that stance, and my general reaction is as follows: #1, Hopelessness/despair cannot be an option, especially for those of us who are outside Gaza. #2, I’m increasingly of the view that “pity” is a patronizing, othering, and somewhat self-paralyzing kind of response to the situation Gaza’s people are facing, under Israel’s truly outrageous genocidal assault.
What I would urge is that those of us outside Gaza should instead view the situation of the people there with a radical and empowering form of empathy for all of them, and with admiration for the steadfastness and resilience they and their society have shown in the face of Israel’s almost unfathomable cruelty.
Continue reading “To the people of Gaza: Empathy and admiration, not ‘pity’”